More like Dancers than Statues
(Introduction to Reversal Theory)
We are more like dancers than statues.
I’d like to spend a few minutes introducing you to a cool little theory that I bet you’re not familiar with. It’s called Reversal Theory and (if you’ll pardon the pun), it’s might just turn things upside down for you.
Let’s start with this – think about the theories of personality you’re most familiar with. Probably Big 5 comes to mind? Maybe Myers-Briggs? Bonus points if Allport or Eysenck popped into your mind first. Here’s the thing – most theories of personality are trait theories. They’re based on how we are, and how we stay the same. They tell us who we are, across time and situations.
Now answer this question: Do you feel like an INFP all day, every day? Aren’t there times when you’re more or less agreeable, more or less open to new experience? (And yes, while all of those theories account for slow, incremental change across the lifespan, that’s not what I mean.) I mean sometimes don’t you feel disagreeable in the morning, and more agreeable after coffee? Don’t you sometimes feel conscientious when you start working on a project and then markedly not conscientious as you slog through it for 5 hours? Don’t you sometimes feel extroverted at the beginning of a party, but just feel yourself retreating to introversion over the course of the evening? This is the aim of Reversal Theory – to give us a structure for thinking about how we are different across time and situations, rather than the same. (Don’t fret! It doesn’t do anything to diminish trait theory – all of that still counts!)
To begin, I need you to imagine a bank of 4 light switches.
Now, I don’t want blow your mind too much right now, but in Reversal Theory, we’re not going to be thinking about traits on a continuum. We’re going to be thinking about 4 pairs of states, and each of them flips off or on like a lightswitch. (No, not like a dimmer-switch. I know the continuum is our best friend in therapy, but hang in here with me. Just wait until the end.)
Here they are:
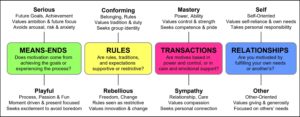
Ok, let’s visit these one by one.
Serious-Playful
You don’t get to be serious and playful at the same time. Wen you’re in the serious state, you’re goal-oriented and future-focused. You’re focused on achieving something important and maybe on the consequences of not getting things done. When you’re driving to work for an 8am meeting with your boss to give an update on the progress of your latest project, chances are you’re in the serious state. But when it’s sunny, breezy, and 75 degrees on a Saturday afternoon, and you don’t have to rush anywhere (and also that favorite song of yours from your junior year in high school comes on the radio) – you’re probably in the playful state. In the playful state, you’re in the moment and focused mostly on enjoyment.
Conforming-Rebellious
When you’re in the conforming state, you’re focused on the value of fitting in, doing what’s right, meeting expectations. Lots of people are in the conforming state at school, work, or church. Teens are often in the conforming state, even when it doesn’t seem like it to parents (e.g., smoking to “be cool” or drinking to “fit in,” even though parents might call that rebellion!). When you’re in the rebellious state, your primary motivation is freedom, or individuality. When you spend Saturday doing whatever you want to do, or when you protest an injustice on your own behalf, or when you get a purple streak in your hair, even though your mother, husband, and coworkers might be scandalized, you’re probably in the rebellious state.
Mastery-Sympathy
In the mastery state, you’re primarily concerned with things like doing better, having control, and making progress. In the sympathy state, you’re mostly concerned with taking it easy, being gentle, love and nurturing. Chance are, if you’re at the gym, you either are in the mastery state or you’d certainly like to be. If you sometimes go to the gym for the “princess package” (a gentle swim, then the whirlpool, then the sauna, and end it with a smoothie), you’re probably in the sympathy state.
Self-Other
The self and other states are probably what you think they are – being focused on you or being focused on someone else. These combine really naturally with the mastery and sympathy states. You might be exercising control and power over self (like when you’re at the gym), or you might be exercising control and power over someone else. For example, you might be bargaining down a salesperson for the best price and you definitely want to “come out on top” or you might really investing in beating your last high score in DoodleJump. That’s self-mastery. But what if you’re tutoring a high school student and really encouraging and empowering them to have control and mastery over themselves and their schoolwork? Any time you function as a teacher, coach, or mentor – you’re probably in the other mastery state, focused on power, control, and mastery…but for someone else. And sympathy works the same way. When you want to eat ice cream to soothe your jangled nerves, take yourself out on a date, choose to watch Netflix instead of push yourself to that deadline, you’re in the self-sympathy states. When you want to give that kind of care, love, and lenience to someone else – helping a friend in need, letting your partner sleep in – you’re in the other-sympathy states.
Now, for each of these states, you are in one or the other of each pair at any given time. You might be more aware of one or two of them, but you’re in all four. And if you combine the states you’re in with the situation you’re in or what you’re doing, you get different and interesting results. So, you may be writing progress notes and be in the SERIOUS-conforming-self-mastery states. If you are, you’re probably killing it, getting work done, feeling great about your progress. But, if you’re in the playful-REBELLIOUS-self-sympathy state trying to work on your progress notes, I bet you’re not making any progress at all. I bet you’re sitting there, miserable, eking out a sentence at a time, wishing you were done, desperate for a massage or a margarita. See, we’re not always in the optimal states for whatever we’re doing at the moment.
OK, that’s as far as I’d like to bring you for right now. I want to give you a teaser…while you wait for the next post on this, think about what states your clients are in while they’re in session with you. Think about what states they might be in when they argue with their partners, when they’re disciplining their kids, sitting in their school desks, trying to resist peer pressure, or captivated by worried thoughts.
(If you are already in love, and don’t want to wait for the next post, buy this book.)
Comment below if you have thoughts or questions!








